Opioid-related overdoses and deaths are at an all-time high. In fact, drug overdose deaths are now the leading cause of accidental death in the United States.1 More than 450,000 people died from drug overdoses involving an opioid from 1999 to 2018.2
History
In the late 1990s, pharmaceutical companies worked hard to convince medical professionals that patients would not become addicted to prescription opioid painkillers. Due to this push, healthcare providers began to prescribe them more. However, it wasn’t clear right away just how addictive these drugs are.3 Though opioids are necessary for palliative care and following major accidents or surgeries, they have become more commonly prescribed for minor issues, such as headaches or back pain. Over the last three decades, as prescriptions for these drugs have been distributed more freely and in higher quantities, we have seen a major rise in misuse, overdoses and deaths as a result.4
Important Terms to Know
- Opioids – Drugs that act on the body’s nervous system to relieve pain.5
- Fentanyl – A powerful synthetic opioid analgesic that is similar to morphine but is 50 to 100 times more potent.6
- Naloxone – A medication designed to rapidly reverse opioid overdose. It binds to opioid receptors in the body to block the effects of other opioids. An example of this is NARCAN®, a nasal spray administered to patients laying on their back.7
- Overdose – When the body has more of a drug (or combination of drugs) in its system than it can handle. This usually happens when a person takes more than the medically recommended dose.8
- Heroin – An addictive, illegal drug processed from morphine.9 80% of heroin users first misused prescription opioid drugs. However, less than 4% of people who misuse prescription opioid drugs go on to use heroin.10
The CDC is a great resource for more important terms defined.
National Statistics
- More than 1,000 people are treated in emergency rooms each day for not using prescription opioids as prescribed.11
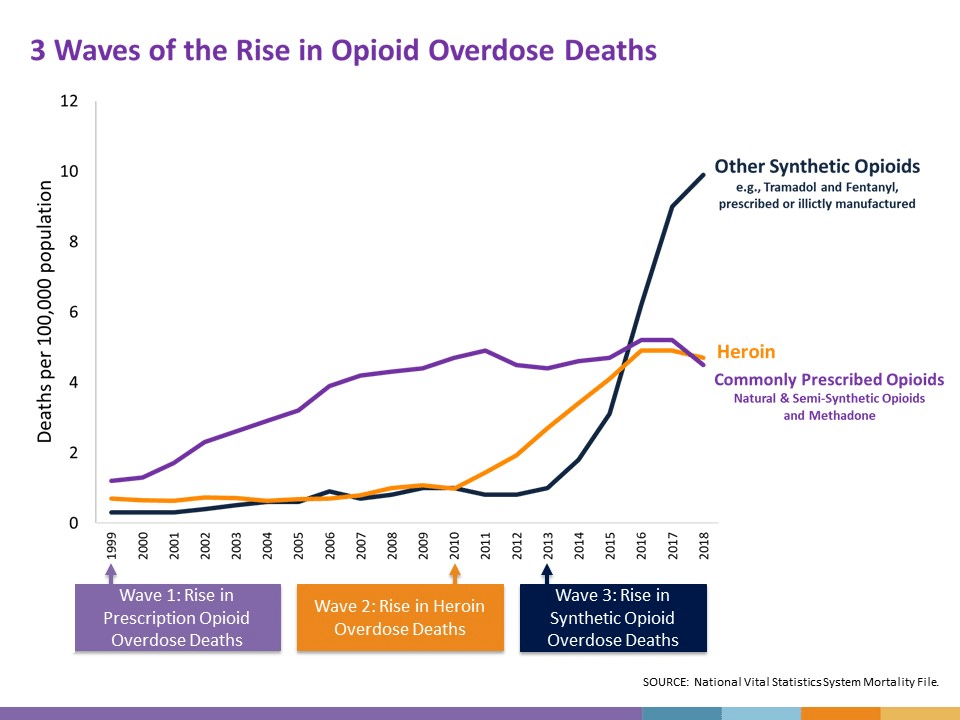
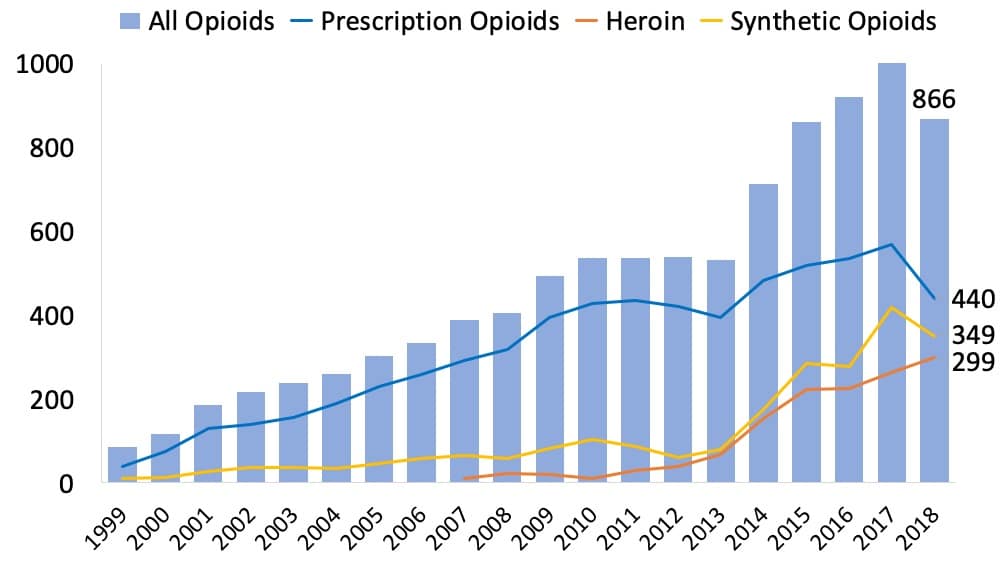
- In 2018, there were 67,367 drug overdose deaths reported in the United States, and opioids were involved in nearly 70% of cases.14
- An average of 41 people die every day from prescription opioid overdoses.11
- Roughly 21-29% of the people who use prescription opioids for chronic pain misuse them.3
Georgia Statistics
- 14.9% of Georgia high school students reported taking prescription painkillers without a doctor’s prescription.12
- In 2006, 31.5% of all overdose deaths in Georgia were caused by opioids. As of 2018, opioids account for more than 60% of drug overdose deaths. 13
- Overdose deaths more than tripled in Georgia between 1999 and 2013, and prescription opioid overdose deaths in Georgia
increased tenfold in the same time period.14
For more Georgia statistics, see this infographic from the Department of Behavioral Health and Developmental Disabilities (DBHDD).
What GUIDE is Doing
GUIDE has focused on this growing epidemic over the last few years by sharing the latest information and research with the community via our Inspired to Make Healthy Choices monthly newsletters, covering topics such as Prescription Drug Misuse, Prescription Drug Disposal, Overdose Prevention and Cleaning Out the Medicine Cabinet. An additional focus has been made on raising community awareness around the DEA’s Prescription Take Back Days each year (held in April and October) and the local drop-off locations for disposing of unused and expired prescription drugs. In addition, we have multiple PSAs related to prescription drug safety.
GUIDE is currently working on a grant funded by DBHDD to address prescription drug misuse and abuse with a focus on the opioid epidemic in DeKalb County. By partnering with several community stakeholders and organizations, our goal is to prevent prescription drug misuse and abuse through capacity building, raising community awareness, delivering resources and expanding prevention efforts.
You can find out more about the prevention of prescription drug misuse and abuse, as well as how you can help address the opioid epidemic, through our many blog posts dedicated to this topic, as well as by following us on social media @guidtgti.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29262202/
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/opioids/opioid-crisis
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/opioids/prescribed.html
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/opioids
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/fentanyl
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/related-topics/opioid-overdose-reversal-naloxone-narcan-evzio
- https://www.overdoseday.com/resources/overdose-basics/
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/heroin/what-heroin
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/heroin
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/data/prescribing/overdose-death-maps.html
- https://nccd.cdc.gov/youthonline/App/Default.aspx
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/opioids/opioid-summaries-by-state/georgia-opioid-involved-deaths-related-harms
- http://www.senate.ga.gov/sro/Documents/StudyCommRpts/OpioidsAppendix.pdf
